The
client logs are located in the %WINDIR%\System32\CCM\Logs folder or %WINDIR%\SysWOW64\CCM\Logs (for x64 OS).
The
SCCM server log files are located in the <INSTALL_PATH>\Logs or SMS_CCM\Logs folder.
IIS logs can be found in %WINDIR%\System32\logfiles\W3SVC1 folder.
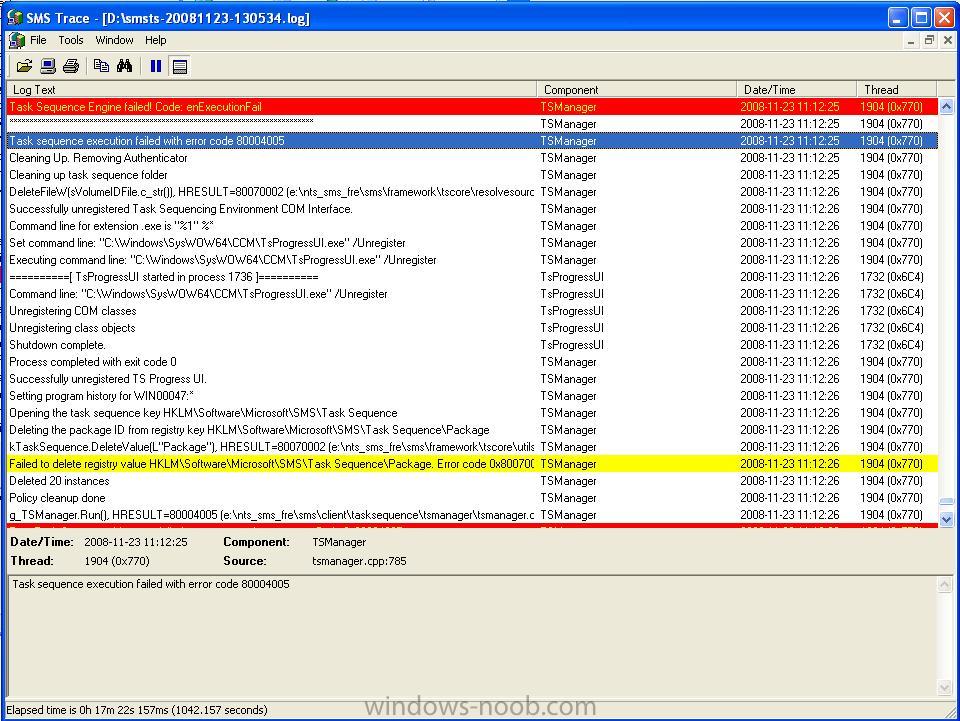
You can use
Trace32.exe found in the
Sccm2007 Toolkit, to interpret the logs easily (errors in Red, warnings in Yellow).
 Client Log Files
Client Log Files* CAS - Content Access Service. Maintains the local package cache.
* Ccmexec.log - Records activities of the client and the SMS Agent Host service.
* CertificateMaintenance.log - Maintains certificates for Active Directory directory service and management points.
* ClientIDManagerStartup.log - Creates and maintains the client GUID.
* ClientLocation.log - Site assignment tasks.
* ContentTransferManager.log - Schedules the Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) or the Server Message Block (SMB) to download or to access SMS packages.
* DataTransferService.log - Records all BITS communication for policy or package access.
* Execmgr.log - Records advertisements that run.
* FileBITS.log - Records all SMB package access tasks.
* Fsinvprovider.log (renamed to FileSystemFile.log in all SMS 2003 Service Packs) - Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) provider for software inventory and file collection.
* InventoryAgent.log - Creates discovery data records (DDRs) and hardware and software inventory records.
* LocationServices.log - Finds management points and distribution points.
* Mifprovider.log - The WMI provider for .MIF files.
* Mtrmgr.log - Monitors all software metering processes.
* PolicyAgent.log - Requests policies by using the Data Transfer service.
* PolicyAgentProvider.log - Records policy changes.
* PolicyEvaluator.log - Records new policy settings.
* Remctrl.log - Logs when the remote control component (WUSER32) starts.
* Scheduler.log - Records schedule tasks for all client operations.
* Smscliui.log - Records usage of the Systems Management tool in Control Panel.
* StatusAgent.log - Logs status messages that are created by the client components.
* SWMTRReportGen.log - Generates a usage data report that is collected by the metering agent. (This data is logged in Mtrmgr.log.)
Server Log Files* Ccm.log - Client Configuration Manager tasks.
* Cidm.log - Records changes to the client settings by the Client Install Data Manager (CIDM).
* Colleval.log - Logs when collections are created, changed, and deleted by the Collection Evaluator.
* Compsumm.log - Records Component Status Summarizer tasks.
* Cscnfsvc.log - Records Courier Sender confirmation service tasks.
* Dataldr.log - Processes Management Information Format (MIF) files and hardware inventory in the Configuration Manager 2007 database.
* Ddm.log - Saves DDR information to the Configuration Manager 2007 database by the Discovery Data Manager.
* Despool.log - Records incoming site-to-site communication transfers.
* Distmgr.log - Records package creation, compression, delta replication, and information updates.
* Hman.log - Records site configuration changes, and publishes site information in Active Directory Domain Services.
* Inboxast.log - Records files that are moved from the management point to the corresponding SMS\INBOXES folder.
* Inboxmgr.log - Records file maintenance.
* Invproc.log - Records the processing of delta MIF files for the Dataloader component from client inventory files.
* Mpcontrol.log - Records the registration of the management point with WINS. Records the availability of the management point every 10 minutes.
* Mpfdm.log - Management point component that moves client files to the corresponding SMS\INBOXES folder.
* MPMSI.log - Management point .msi installation log.
* MPSetup.log - Records the management point installation wrapper process.
* Ntsvrdis.log - Configuration Manager 2007 server discovery.
* Offermgr.log - Records advertisement updates.
* Offersum.log - Records summarization of advertisement status messages.
* Policypv.log - Records updates to the client policies to reflect changes to client settings or advertisements.
* Replmgr.log - Records the replication of files between the site server components and the Scheduler component.
* Rsetup.log - Reporting point setup log.
* Sched.log - Records site-to-site job and package replication.
* Sender.log - Records files that are sent to other child and parent sites.
* Sinvproc.log - Records client software inventory data processing to the site database in Microsoft SQL Server.
* Sitecomp.log - Records maintenance of the installed site components.
* Sitectrl.log - Records site setting changes to the Sitectrl.ct0 file.
* Sitestat.log - Records the monitoring process of all site systems.
* Smsdbmon.log - Records database changes.
* Smsexec.log - Records processing of all site server component threads.
* Smsprov.log - Records WMI provider access to the site database.
* SMSReportingInstall.log - Records the Reporting Point installation. This component starts the installation tasks and processes configuration changes.
* SMSSHVSetup.log - Records the success or failure (with failure reason) of installing the System Health Validator point.
* Srvacct.log - Records the maintenance of accounts when the site uses standard security.
* Statmgr.log - Writes all status messages to the database.
* Swmproc.log - Processes metering files and maintains settings.
Admin Console Log Files* RepairWizard.log - Records errors, warnings, and information about the process of running the Repair Wizard.
* ResourceExplorer.log - Records errors, warnings, and information about running the Resource Explorer.
* SMSAdminUI.log - Records the local Configuration Manager 2007 console tasks when you connect to Configuration Manager 2007 sites.
Management Point Log Files* MP_Ddr.log - Records the conversion of XML.ddr records from clients, and copies them to the site server.
* MP_GetAuth.log - Records the status of the site management points.
* MP_GetPolicy.log - Records policy information.
* MP_Hinv.log - Converts XML hardware inventory records from clients and copies the files to the site server.
* MP_Location.log - Records location manager tasks.
* MP_Policy.log - Records policy communication.
* MP_Relay.log - Copies files that are collected from the client.
* MP_Retry.log - Records the hardware inventory retry processes.
* MP_Sinv.log - Converts XML hardware inventory records from clients and copies them to the site server.
* MP_Status.log - Converts XML.svf status message files from clients and copies them to the site server.
Mobile Device Management Log Files* DmClientHealth.log - Records the GUIDs of all the mobile device clients that are communicating with the Device Management Point.
* DmClientRegistration.log - Records registration requests from and responses to the mobile device client in Native mode.
* DmpDatastore.log - Records all the site database connections and queries made by the Device Management Point.
* DmpDiscovery.log - Records all the discovery data from the mobile device clients on the Device Management Point.
* DmpFileCollection.log - Records mobile device file collection data from mobile device clients on the Device Management Point.
* DmpHardware.log - Records hardware inventory data from mobile device clients on the Device Management Point.
* DmpIsapi.log - Records mobile device communication data from device clients on the Device Management Point.
* dmpMSI.log - Records the MSI data for Device Management Point setup.
* DMPSetup.log - Records the mobile device management setup process.
* DmpSoftware.log - Records mobile device software distribution data from mobile device clients on the Device Management Point.
* DmpStatus.log - Records mobile device status messages data from mobile device clients on the Device Management Point.
* FspIsapi.log - Records Fallback Status Point communication data from mobile device clients and client computers on the Fallback Status Point.
Mobile Device Client Log Files* DmCertEnroll.log - Records certificate enrollment data on mobile device clients.
* DMCertResp.htm (in \temp) - Records HTML response from the certificate server when the mobile device Enroller program requests a client authentication certificate on mobile device clients.
* DmClientSetup.log - Records client setup data on mobile device clients.
* DmClientXfer.log - Records client transfer data for Windows Mobile Device Center and ActiveSync deployments.
* DmCommonInstaller.log - Records client transfer file installation for setting up mobile device client transfer files on client computers.
* DmInstaller.log - Records whether DMInstaller correctly calls DmClientSetup and whether DmClientSetup exits with success or failure on mobile device clients.
* DmInvExtension.log - Records Inventory Extension file installation for setting up Inventory Extension files on client computers.
* DmSvc.log - Records mobile device management service data on mobile device clients.
Operating System Deployment Log Files* CCMSetup.log - Provides information about client-based operating system actions.
* CreateTSMedia.log - Provides information about task sequence media when it is created. This log is generated on the computer running the Configuration Manager 2007 administrator console.
* DriverCatalog.log - Provides information about device drivers that have been imported into the driver catalog.
* MP_ClientIDManager.log - Provides information about the Configuration Manager 2007 management point when it responds to Configuration Manager 2007 client ID requests from boot media or PXE. This log is generated on the Configuration Manager 2007 management point.
* MP_DriverManager.log - Provides information about the Configuration Manager 2007 management point when it responds to a request from the Auto Apply Driver task sequence action. This log is generated on the Configuration Manager 2007 management point.
* MP_Location.log - Provides information about the Configuration Manager 2007 management point when it responds to request state store or release state store requests from the state migration point. This log is generated on the Configuration Manager 2007 management point.
* Pxecontrol.log - Provides information about the PXE Control Manager.
* PXEMsi.log - Provides information about the PXE service point and is generated when the PXE service point site server has been created.
* PXESetup.log - Provides information about the PXE service point and is generated when the PXE service point site server has been created.
* Setupact.log Setupapi.log Setuperr.log Provide information about Windows Sysprep and setup logs.
* SmpIsapi.log - Provides information about the state migration point Configuration Manager 2007 client request responses.
* Smpmgr.log - Provides information about the results of state migration point health checks and configuration changes.
* SmpMSI.log - Provides information about the state migration point and is generated when the state migration point site server has been created.
* Smsprov.log - Provides information about the SMS provider.
* Smspxe.log - Provides information about the Configuration Manager 2007 PXE service point.
* SMSSMPSetup.log - Provides information about the state migration point and is generated when the state migration point site server has been created.
* Smsts.log - General location for all operating system deployment and task sequence log events.
* TaskSequenceProvider.log - Provides information about task sequences when they are imported, exported, or edited.
* USMT Log loadstate.log - Provides information about the User State Migration Tool (USMT) regarding the restore of user state data.
* USMT Log scanstate.log - Provides information about the USMT regarding the capture of user state data.
Network Access Protection Log Files* Ccmcca.log - Logs the processing of compliance evaluation based on Configuration Manager NAP policy processing and contains the processing of remediation for each software update required for compliance.
* CIAgent.log - Tracks the process of remediation and compliance. However, the software updates log file, *Updateshandler.log - provides more informative details on installing the software updates required for compliance.
* locationservices.log - Used by other Configuration Manager features (for example, information about the client’s assigned site) but also contains information specific to Network Access Protection when the client is in remediation. It records the names of the required remediation servers (management point, software update point, and distribution points that host content required for compliance), which are also sent in the client statement of health.
* SDMAgent.log - Shared with the Configuration Manager feature desired configuration management and contains the tracking process of remediation and compliance. However, the software updates log file, Updateshandler.log, provides more informative details about installing the software updates required for compliance.
* SMSSha.log - The main log file for the Configuration Manager Network Access Protection client and contains a merged statement of health information from the two Configuration Manager components: location services (LS) and the configuration compliance agent (CCA). This log file also contains information about the interactions between the Configuration Manager System Health Agent and the operating system NAP agent, and also between the Configuration Manager System Health Agent and both the configuration compliance agent and the location services. It provides information about whether the NAP agent successfully initialized, the statement of health data, and the statement of health response.
System Health Validator Point Log Files* Ccmperf.log -Contains information about the initialization of the System Health Validator point performance counters.
* SmsSHV.log - The main log file for the System Health Validator point; logs the basic operations of the System Health Validator service, such as the initialization progress.
* SmsSHVADCacheClient.log - Contains information about retrieving Configuration Manager health state references from Active Directory Domain Services.
* SmsSHVCacheStore.log - Contains information about the cache store used to hold the Configuration Manager NAP health state references retrieved from Active Directory Domain Services, such as reading from the store and purging entries from the local cache store file. The cache store is not configurable.
* SmsSHVRegistrySettings.log - Records any dynamic changes to the System Health Validator component configuration while the service is running.
* SmsSHVQuarValidator.log - Records client statement of health information and processing operations. To obtain full information, change the registry key LogLevel from 1 to 0 in the following location:HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SMSSHV\Logging\@GLOBAL
Desired Configuration Management Log Files* ciagent.log - Provides information about downloading, storing, and accessing assigned configuration baselines.
* dcmagent.log - Provides high-level information about the evaluation of assigned configuration baselines and desired configuration management processes.
* discovery.log - Provides detailed information about the Service Modeling Language (SML) processes.
* sdmagent.log - Provides information about downloading, storing, and accessing configuration item content.
* sdmdiscagent.log - Provides high-level information about the evaluation process for the objects and settings configured in the referenced configuration items.
Wake On LAN Log Files* Wolmgr.log - Contains information about wake-up procedures such as when to wake up advertisements or deployments that are configured for Wake On LAN.
* WolCmgr.log - Contains information about which clients need to be sent wake-up packets, the number of wake-up packets sent, and the number of wake-up packets retried.
Software Updates Site Server Log Files* ciamgr.log - Provides information about the addition, deletion, and modification of software update configuration items.
* distmgr.log - Provides information about the replication of software update deployment packages.
* objreplmgr.log - Provides information about the replication of software updates notification files from a parent to child sites.
* PatchDownloader.log - Provides information about the process for downloading software updates from the update source specified in the software updates metadata to the download destination on the site server.
* replmgr.log - Provides information about the process for replicating files between sites.
* smsdbmon.log - Provides information about when software update configuration items are inserted, updated, or deleted from the site server database and creates notification files for software updates components.
* SUPSetup - Provides information about the software update point installation. When the software update point installation completes, Installation was successful is written to this log file.
* WCM.log - Provides information about the software update point configuration and connecting to the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) server for subscribed update categories, classifications, and languages.
* WSUSCtrl.log - Provides information about the configuration, database connectivity, and health of the WSUS server for the site.
* wsyncmgr.log -Provides information about the software updates synchronization process.
WSUS Server Log Files* Change.log - Provides information about the WSUS server database information that has changed.
* SoftwareDistribution.log - Provides information about the software updates that are synchronized from the configured update source to the WSUS server database.
Software Updates Client Computer Log Files* CAS.log - Provides information about the process of downloading software updates to the local cache and cache management.
* CIAgent.log - Provides information about processing configuration items, including software updates.
* LocationServices.log - Provides information about the location of the WSUS server when a scan is initiated on the client.
* PatchDownloader.log - Provides information about the process for downloading software updates from the update source to the download destination on the site server. This log is only on the client computer configured as the synchronization host for the Inventory Tool for Microsoft Updates.
* PolicyAgent.log - Provides information about the process for downloading, compiling, and deleting policies on client computers.
* PolicyEvaluator - Provides information about the process for evaluating policies on client computers, including policies from software updates.
* RebootCoordinator.log - Provides information about the process for coordinating system restarts on client computers after software update installations.
* ScanAgent.log - Provides information about the scan requests for software updates, what tool is requested for the scan, the WSUS location, and so on.
* ScanWrapper - Provides information about the prerequisite checks and the scan process initialization for the Inventory Tool for Microsoft Updates on Systems Management Server (SMS) 2003 clients.
* SdmAgent.log - Provides information about the process for verifying and decompressing packages that contain configuration item information for software updates.
* ServiceWindowManager.log - Provides information about the process for evaluating configured maintenance windows.
* smscliUI.log - Provides information about the Configuration Manager Control Panel user interactions, such as initiating a Software Updates Scan Cycle from the Configuration Manager Properties dialog box, opening the Program Download Monitor, and so on.
* SmsWusHandler - Provides information about the scan process for the Inventory Tool for Microsoft Updates on SMS 2003 client computers.
* StateMessage.log - Provides information about when software updates state messages are created and sent to the management point.
* UpdatesDeployment.log - Provides information about the deployment on the client, including software update activation, evaluation, and enforcement. Verbose logging shows additional information about the interaction with the client user interface.
* UpdatesHandler.log - Provides information about software update compliance scanning and about the download and installation of software updates on the client.
* UpdatesStore.log - Provides information about the compliance status for the software updates that were assessed during the compliance scan cycle.
* WUAHandler.log - Provides information about when the Windows Update Agent on the client searches for software updates.
* WUSSyncXML.log - Provides information about the Inventory Tool for the Microsoft Updates synchronization process. This log is only on the client computer configured as the synchronization host for the Inventory Tool for Microsoft Updates.
Windows Update Agent Log File* WindowsUpdate.log - Provides information about when the Windows Update Agent connects to the WSUS server and retrieves the software updates for compliance assessment and whether there are updates to the agent components.



